Alopecia is the general medical term for hair loss. There are many types of hair loss with different symptoms and causes.
Some of the more common types of hair loss, including male- and female- pattern baldness, alopecia areata, scarring alopecia, anagen effluvium, and telogen effluvium.
Pattern baldness – Male-pattern baldness is the most common type of hair loss, affecting around half of all men by the age of 50. It generally follows a pattern of a receding hairline, followed by thinning of the hair on the crown and temples, leaving a horseshoe shape around the back and sides of the head.
Sometimes it can progress to complete baldness, although this is uncommon.
As well as affecting men, it can sometimes affect women (female-pattern baldness). In female-pattern baldness, hair usually only thins on top of the head.
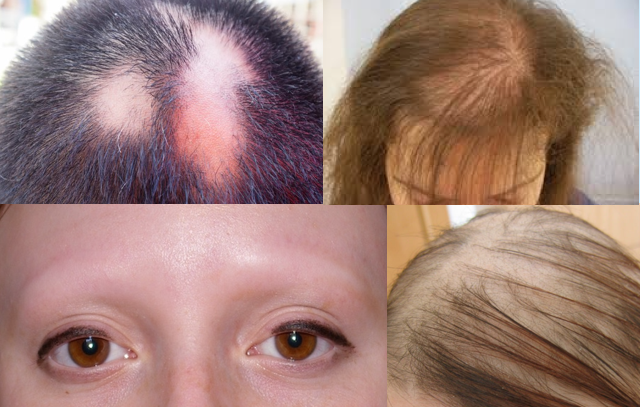
Alopecia areata – causes patches of baldness about the size of a large coin. They usually appear on the scalp but can occur anywhere on the body. It can occur at any age, but mostly affects teenagers and young adults. In most cases of alopecia areata, hair will grow back in a few months. Alopecia areata is caused by a problem with the immune system (the body’s natural defence against infection and illness).
Some people go on to develop a more severe form of hair loss, such as:
- Alopecia totalis (no scalp hair)
- Alopecia universalis (no hair on the scalp and body, including eyebrows and eyelashes)