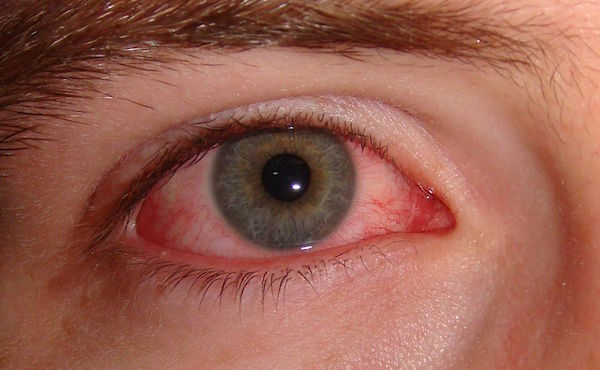
Chlamydial Inclusion Conjunctivitis is an infection of the conjunctiva of the eye that is caused by the sexually transmitted disease called Chlamydia.
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection. It is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Most people with chlamydia don’t notice any symptoms and don’t know they have it. In the eyes, chlamydia can cause irritation, pain, swelling and discharge similar to conjunctivitis. These symptoms continue for several weeks until treatment is started. Most often, patients with chlamydial conjunctivitis will have an associated genital infection (of which they may be unaware).
Chlamydia, specifically Chlamydia trachomatis, is a human pathogen that is one of three bacterial species in the Chlamydial family.
Chlamydia is spread from person-to-person during unprotected sex. It can be passed to the eye by a hand or other body part with the infected bacteria. Chlamydia cannot be spread by kissing, toilet seats, door knobs, swimming pools, sharing clothes or eating utensils.