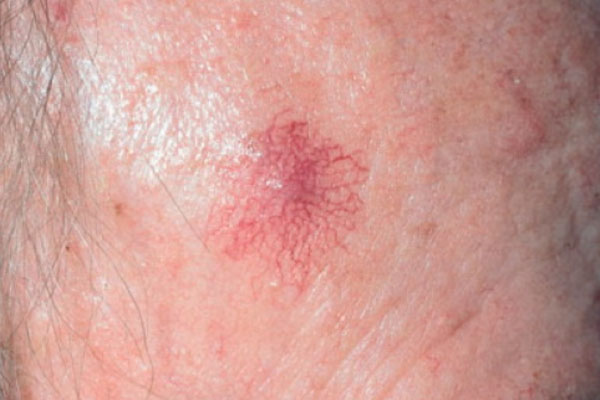
A spider angioma is an enlarged blood vessel in the skin (resembling the body of a spider), from which smaller blood vessels extend (resembling the spider’s legs). It has also been called “naevus araneus”, “vascular spider”, “arterial spider”, “spider telangiectasia” and “spider naevus/nevus”.
Some of these names are Latin: “araneus” for “spider”, “angioma” for “blood vessel” and “telangiectasia” for “enlarged blood vessel”. “Naevus” means an increase in normal or healthy tissue within the skin.
The cause of spider angiomas is not known. The vast majority affect healthy people, and most people have only one spider angioma or a just a few. Spider angiomas may appear when the body has increased levels of oestrogen hormones such as in pregnancy or when taking the oral contraceptive pill. They may also occasionally occur in patients with liver or thyroid disease.